
The new_branch branch has a tracking branch of. In a standard setup, you generally have an origin and an upstream remote the latter being the gatekeeper of the project or the source of truth to which you wish to contribute. The test branch has a tracking branch of. Git upstream: Keep up-to-date and contribute Let me start by detailing a common setup and the most basic workflow to interact with upstream repositories. The main branch has a tracking branch of. Set upstream branch using the git push command with the -u extension or use the longer version -set-upstream. Switch to it using the checkout command with the -b. Now, you can list all your branches that are tracking upstream branches using “Git branch” with the -vv option: git branch -vv Method 1: Set Upstream Branch Using Git Push 1.
#Git set upstream how to#
How to check which Git Branches are tracking which Upstream Branches The terminal prints out the confirmation message:
None of these answers cover how i do it (in complete form) so here it is: git push -u originThis will also create an upstream branch if one does not exist. org :my-user/some-project. org :my-user/some-project.git (fetch) origin git bitbucket. Now, you need to track a new upstream branch than the one you just setup running: git branch -u įor example: git branch main -u git branch main -u The -u flag is specifying that you want to link your local branch to the upstream branch. First, verify that you have already setup a remote for the upstream repository, and hopefully an origin too: git remote -v origin git bitbucket. git push -u origin Īlternatively, you can use the ‘–set-upstream’ command as well to set the Upstream branch git push -set-upstream origin Now, you need to set the upstream branch using the Git push command with the -u option.
#Git set upstream software#
You will mostly apply git set upstream when creating a repo or collaborating with other software engineers on a forked repo for the first time. When the current branch i.e (‘new_branch’) has no Upstream branch set and we try to run the command “Git push”. Getting started with git set upstream Git upstream is a link between the local repo and the remote one, and it enables you to synchronize the two repos.
#Git set upstream install#
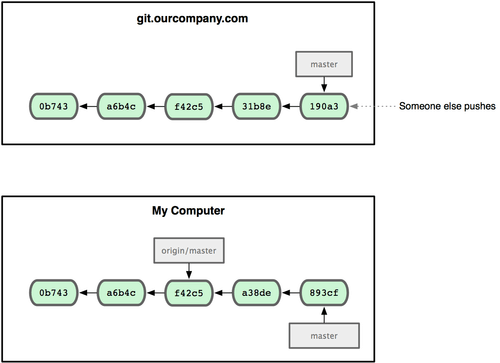
How to Install Python Packages for AWS Lambda Layers? By using this command you can setup tracking information for the current branch during the push.Best Way to Master Spring Boot – A Complete Roadmap.Java Developer Learning Path – A Complete Roadmap.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.# and have 2 and 3 different commits each, respectively. # Your branch and 'origin/development' have diverged, Git tells you about this right in the output for "git status": $ git status This information helps tremendously in staying up-to-date. Create a new branch with the name and switch to the current branch using the -b option. Set Upstream Branch using Git Push command. (b) if there are 4 commits on the remote upstream branch which you haven't pulled yet, then your local branch is "4 commits behind" its upstream branch. Using the Git Push command with the -u option for the upstream branch. (a) if you have 2 commits in your local repository which you haven't pushed to the remote yet, then your local branch is "2 commits ahead" of its upstream branch. Git can now also tell you about unsynced commits which you haven't pushed or pulled, yet. With an upstream branch set, you can simply use the shorthand commands "git pull" and "git push" - instead of having to think about the exact parameters like in "git push origin development". This relationship is very helpful for two reasons: Let's also say that you've set the remote "origin/development" as its upstream branch. Let's say that your current local HEAD branch is named "development".

Why should you set up an upstream branch for a local branch? In practice, however, in makes lots of sense to see them as counterparts - connected in a so-called "tracking connection". In theory, local and remote branches in Git are completely separate items.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
